ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS
INTRODUCTION
Python has provided us a group of built-in methods for List manipulation. Below are the methods for adding new elements in the list.
append() method
append() method is used to add a new element in the list. By using append() method we can add only one record at a time. If we add multiple records at a time then Python will raise error.
# append() method example 1
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
print("\nElement of list str_list ->", str_list)
str_list.append('Word')
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
Revised element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML', 'Word']
In the above example, we have added one new element Word in the list using append() method.
# append() method example 2
int_list = [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20]
print("\nElement of list int_list ->", int_list)
int_list.append(12)
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list int_list -> [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20]
Revised element of list int_list -> [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20, 12]
In the above example, we have added one new element 12 in the list using append() method.
Now we are adding multiple elements by calling append() method multiple times.
# append() method example 3
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
print("\nElement of list str_list ->", str_list)
str_list.append('Word')
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
str_list.append('Excel')
str_list.append('VB .Net')
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
Revised element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML', 'Word']
Revised element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML', 'Word', 'Excel', 'VB .Net']
# append() method example 4
int_list = [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20]
print("\nElement of list int_list ->", int_list)
int_list.append(12)
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
int_list.append(5)
int_list.append(7)
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list int_list -> [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20]
Revised element of list int_list -> [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20, 12]
Revised element of list int_list -> [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20, 12, 5, 7]
If we try to pass multiple values in the append() method then Python will raise an error.
# append() method example 5
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
print("\nElement of list str_list ->", str_list)
str_list.append('Word')
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
str_list.append('Excel', 'VB .Net')
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
Revised element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML', 'Word']
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:\PYTHON\PROGRAM\tempCodeRunnerFile.python", line 13, in <module>
str_list.append('Excel', 'VB .Net')
TypeError: list.append() takes exactly one argument (2 given)
# append() method example 6
int_list = [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20]
print("\nElement of list int_list ->", int_list)
int_list.append(12)
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
int_list.append(5, 7)
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list int_list -> [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20]
Revised element of list int_list -> [4, 2, 6, 10, 15, 20, 12]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:\PYTHON\PROGRAM\tempCodeRunnerFile.python", line 13, in <module>
int_list.append(5, 7)
TypeError: list.append() takes exactly one argument (2 given)
insert() method
insert() method allows us to add one element in a specific position in the list. If we add the element in the middle of a list then it will shift the previous element of that position to the right.
# insert() method example 1
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
print("\nElement of list str_list ->", str_list)
print("\nCount of element of list str_list ->", len(str_list))
str_list.insert(2, 'Word')
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
print("\nCount of element of list str_list ->", len(str_list))
str_list.insert(4, 'Excel')
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
print("\nCount of element of list str_list ->", len(str_list))
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
Count of element of list str_list -> 6
Revised element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'Word', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
Count of element of list str_list -> 7
Revised element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'Word', 'C++', 'Excel', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
Count of element of list str_list -> 8
In the above example, we can see that we have added the Word element at the position 2 starting from 0. Earlier C++ was at position 2 but after inserting Word, C++ has been shifted to the right. Similarly, Excel element was inserted at position 4. Earlier C was at position 4 which is now replaced by Excel and shifted to the right.
# insert() method example 2
int_list = [400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 200]
print("\nElement of list int_list ->", int_list)
int_list.insert(3, 120)
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
int_list.insert(5, 700)
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list int_list -> [400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 200]
Revised element of list int_list -> [400, 200, 600, 120, 100, 150, 200]
Revised element of list int_list -> [400, 200, 600, 120, 100, 700, 150, 200]
In the above example, 120 has been inserted at the index position 3 where 100 was placed earlier. Now 100 has been shifted to the right. Then 700 has been inserted at the index position 5 where 150 was placed earlier. Now 150 has been shifted to the right.
extend() method
If we want to add more than elements at a time in a list, then we will use the extend() method.
# extend() method example 1
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
print("\nElement of list str_list ->", str_list)
print("\nCount of element of list str_list ->", len(str_list))
str_list.extend(['Word', 'Excel'])
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
print("\nCount of element of list str_list ->", len(str_list))
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
Count of element of list str_list -> 6
Revised element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML', 'Word', 'Excel']
Count of element of list str_list -> 8
In the above example, we have added two elements Word and Excel at a time by using extend() method.
# extend() method example 2
int_list = [400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 200]
print("\nElement of list int_list ->", int_list)
print("\nNumber of element in the list int_list ->", len(int_list))
int_list.extend([300, 120, 700])
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
print("\nRevised Number of element in the list int_list ->", len(int_list))
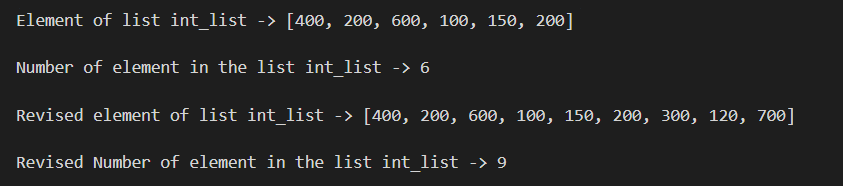
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list int_list -> [400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 200]
Number of element in the list int_list -> 6
Revised element of list int_list -> [400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 200, 300, 120, 700]
Revised Number of element in the list int_list -> 9
In the above example, we have added 3 new elements 300, 120, 700 by using extend() method.
Addition Operator(+)
We can use addition operator to add new elements in an existing list.
# Addition operator example 1
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
print("\nElement of list str_list ->", str_list)
print("\nCount of element of list str_list ->", len(str_list))
str_list_new = ['Word', 'Excel']
str_list = str_list + str_list_new
print("\nRevised element of list str_list ->", str_list)
print("\nCount of element of list str_list ->", len(str_list))
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML']
Count of element of list str_list -> 6
Revised element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML', 'Word', 'Excel']
Count of element of list str_list -> 8
In the above example, we can see that we have created one list variable str_list. Then another list variable str_list_new is created and its elements are included in the list list_str.
# Addition operator example 2
int_list = [400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 200]
print("\nElement of list int_list ->", int_list)
print("\nNumber of element in the list int_list ->", len(int_list))
int_list_new = [300, 120, 700]
int_list = int_list + int_list_new
print("\nRevised element of list int_list ->", int_list)
print("\nRevised Number of element in the list int_list ->", len(int_list))
ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS : Output
Element of list int_list -> [400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 200]
Number of element in the list int_list -> 6
Revised element of list int_list -> [400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 200, 300, 120, 700]
Revised Number of element in the list int_list -> 9
In the above example, we can see that, the list int_list_new has been added with list int_list using addition operator (+). Finally, the list int_list is showing the combined data of int_list and int_list_new.
RELATED TOPICS:
- INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS
- ACCESSING PYTHON LISTS
- UPDATING PYTHON LISTS
- REMOVING ELEMENT IN THE LISTS
- PYTHON LIST SLICING OPERATION
- USING STEP SIZE IN LIST SLICING OPERATION
- LIST SORTING OPERATIONS
- PYTHON LIST BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS
- REMOVING DUPLICATES USING PYTHON SET OPERATOR
- PYTHON SHALLOW COPY OPERATIONS
- PYTHON LIST DEEP COPY
Pingback: PYTHON LIST SHALLOW COPY - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming