PYTHON TUPLE SORTING OPERATIONS
INTRODUCTIONS
Python tuples can be sorted either in forward or backward direction by using below methods:
- sorted() FUNCTION
- SLICING OPERATOR ([:])
sorted() FUNCTION
Sorting an integer tuple
sorted() FUNCTION helps us to sort the tuple in ascending order.
# Tuple sorting by using sorted() example 1
int_tuple = (400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 500)
print("\nField of original tuple ->", int_tuple)
sorted_tuple = sorted(int_tuple)
print("\nField of sorted tuple ->", sorted_tuple)
PYTHON TUPLE SORTING OPERATIONS : Output
Field of original tuple -> (400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 500)
Field of sorted tuple -> [100, 150, 200, 400, 500, 600]
Sorting a string tuple
# Tuple sorting by using sorted() example 2
str_tuple = ('Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML')
print("\nField of original tuple ->", str_tuple)
sorted_tuple = sorted(str_tuple)
print("\nField of sorted tuple ->", sorted_tuple)
PYTHON TUPLE SORTING OPERATIONS : Output
Field of original tuple -> ('Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML')
Field of sorted tuple -> ['C', 'C++', 'Java', 'PHP', 'Python', 'XML']
Sorting a mixed tuple
Sorting is only possible within same data types. It can not be done for mixed tuple.
# Tuple sorting by using sorted() example 3
mixed_tuple = (400, 200, 'Python', 'Java', 5.8, True, 150.65)
print("\nField of original tuple ->", mixed_tuple)
sorted_tuple = sorted(mixed_tuple)
print("\nField of sorted tuple ->", sorted_tuple)
PYTHON TUPLE SORTING OPERATIONS : Output
Field of original tuple -> (400, 200, 'Python', 'Java', 5.8, True, 150.65)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:\PYTHON\PROGRAM\tempCodeRunnerFile.py", line 6, in <module>
sorted_tuple = sorted(mixed_tuple)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
TypeError: '<' not supported between instances of 'str' and 'int'
Sorting a Nested tuple
# Tuple sorting by using sorted() example 4
nested_int_tuple = ((700, 200, 600), (500, 200, 150))
print("\nField of original tuple ->", nested_int_tuple)
sorted_tuple = sorted(nested_int_tuple)
print("\nField of sorted tuple ->", tuple(sorted_tuple))
nested_str_tuple = (('Python', 'Java', 'PHP'), ('C++', 'XML', 'C'))
print("\nField of original tuple ->", nested_str_tuple)
sorted_tuple = sorted(nested_str_tuple)
print("\nField of sorted tuple ->", sorted_tuple)
nested_float_tuple = ((5.9, 2.8, 6.5), (4.2, 2.7, 15.8))
print("\nField of original tuple ->", nested_float_tuple)
sorted_tuple = sorted(nested_float_tuple)
print("\nField of sorted tuple ->", sorted_tuple)
nested_bool_tuple = ((True, False, True), (False, True, False))
print("\nField of original tuple ->", nested_bool_tuple)
sorted_tuple = sorted(nested_bool_tuple)
print("\nField of sorted tuple ->", sorted_tuple)
PYTHON TUPLE SORTING OPERATIONS : Output
Field of original tuple -> ((700, 200, 600), (500, 200, 150))
Field of sorted tuple -> ((500, 200, 150), (700, 200, 600))
Field of original tuple -> (('Python', 'Java', 'PHP'), ('C++', 'XML', 'C'))
Field of sorted tuple -> [('C++', 'XML', 'C'), ('Python', 'Java', 'PHP')]
Field of original tuple -> ((5.9, 2.8, 6.5), (4.2, 2.7, 15.8))
Field of sorted tuple -> [(4.2, 2.7, 15.8), (5.9, 2.8, 6.5)]
Field of original tuple -> ((True, False, True), (False, True, False))
Field of sorted tuple -> [(False, True, False), (True, False, True)]
SLICING OPERATOR ([::])
With slicing operator we can reverse tuple fields. If the tuple fields are sorted with sorted() then we can sort the tuple in descending order by using negative step size.
Tuple reversing using slicing operator
# Tuple sorting by using slicing operator([:]) example 1
int_tuple = (400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 500)
print("\nFields of original tuple ->", int_tuple)
int_tuple_slice = int_tuple[::-1]
print("\nFields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 0->", int_tuple_slice[0])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 1->", int_tuple_slice[1])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 2->", int_tuple_slice[2])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 3->", int_tuple_slice[3])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 4->", int_tuple_slice[4])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 5->", int_tuple_slice[5])
PYTHON TUPLE SORTING OPERATIONS : Output
Fields of original tuple -> (400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 500)
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 0-> 500
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 1-> 150
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 2-> 100
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 3-> 600
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 4-> 200
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 5-> 400
Tuple sorting in descending order
# Tuple sorting by using slicing operator([:]) example 2
int_tuple = (400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 500)
print("\nFields of original tuple ->", int_tuple)
int_tuple_slice = sorted(int_tuple)
print("\nFields of sorted tuple in ascending order ->", int_tuple_slice)
int_tuple_slice = int_tuple_slice[::-1]
print("\nFields of sorted tuple in descending order->", int_tuple_slice)
print("\nFields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 0->", int_tuple_slice[0])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 1->", int_tuple_slice[1])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 2->", int_tuple_slice[2])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 3->", int_tuple_slice[3])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 4->", int_tuple_slice[4])
print("Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 5->", int_tuple_slice[5])
PYTHON TUPLE SORTING OPERATIONS : Output
Fields of original tuple -> (400, 200, 600, 100, 150, 500)
Fields of sorted tuple in ascending order -> [100, 150, 200, 400, 500, 600]
Fields of sorted tuple in descending order-> [600, 500, 400, 200, 150, 100]
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 0-> 600
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 1-> 500
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 2-> 400
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 3-> 200
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 4-> 150
Fields of tuple int_tuple_slice at index 5-> 100
# Tuple sorting by using slicing operator([:]) example 3
str_tuple = ('Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML')
print("\nFields of original tuple ->", str_tuple)
str_tuple_slice = sorted(str_tuple)
print("\nFields of sorted tuple in ascending order ->", str_tuple_slice)
str_tuple_slice = str_tuple_slice[::-1]
print("\nFields of sorted tuple in descending order->", str_tuple_slice)
print("\nFields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 0->", str_tuple_slice[0])
print("Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 1->", str_tuple_slice[1])
print("Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 2->", str_tuple_slice[2])
print("Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 3->", str_tuple_slice[3])
print("Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 4->", str_tuple_slice[4])
print("Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 5->", str_tuple_slice[5])
PYTHON TUPLE SORTING OPERATIONS : Output
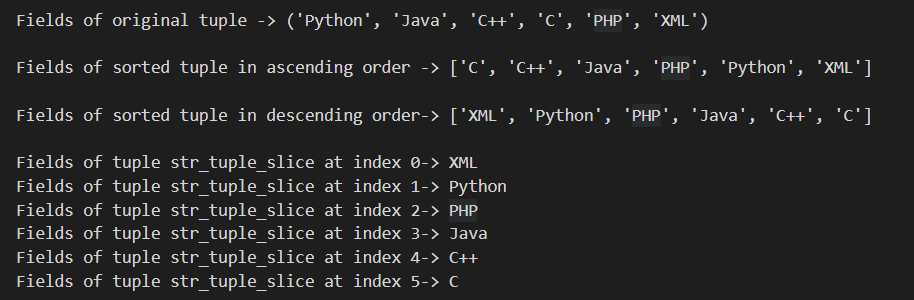
Fields of original tuple -> ('Python', 'Java', 'C++', 'C', 'PHP', 'XML')
Fields of sorted tuple in ascending order -> ['C', 'C++', 'Java', 'PHP', 'Python', 'XML']
Fields of sorted tuple in descending order-> ['XML', 'Python', 'PHP', 'Java', 'C++', 'C']
Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 0-> XML
Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 1-> Python
Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 2-> PHP
Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 3-> Java
Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 4-> C++
Fields of tuple str_tuple_slice at index 5-> C
In the above example, we have seen that both the integer and string tuple are sorted in descending order by using negative step size.
RELATED TOPICS:
- INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON TUPLE
- ACCESSING NUMBER TUPLE IN PYTHON
- ACCESSING STRING TUPLE IN PYTHON
- ACCESSING MIXED TUPLE IN PYTHON
- ACCESSING NESTED TUPLE IN PYTHON
- PYTHON TOUPLE SLICING OPERATION
- STEP SIZE IN PYTHON TUPLE SLICING
- IMMUTABILITY OF TUPLE IN PYTHON
- ZIP FUNCTION IN PYTHON TUPLE
- PYTHON TUPLE BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS
- REOVING TUPLE DUPLICATES USING SET
- PYTHON TUPLE SHALLOW COPY
- PYTHON TUPLE DEEP COPY
Pingback: PYTHON TUPLE BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming