INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS
INTRODUCTION
- Lists in Python are ordered set of elements.
- List elements are mutable, i.e. we can change the elements in the list
- List can store elements of different data types like integer, decimal, string, boolean, another list, sets etc.
- They are enclosed within square brackets([]).
- If there is no element in the list then square bracket will be empty.
- List in Python can contain duplicate elements
LIST ELEMENT DATA TYPE
Checking the data type of a list.
# LIST data type example
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C', 'C++', 'XML', 'PHP']
print("\nData type of list str_list -> ", type(str_list))
print("\nElement of list str_list -> ", str_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
Data type of list str_list -> <class 'list'>
Element of list str_list -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C', 'C++', 'XML', 'PHP']
Data type of elements in the list can be of any data type.
STRING LIST
String lists containing all the string elements.
# String list example
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C', 'C++', 'XML', 'PHP']
print("\nString list contains -> ", str_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
String list contains -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C', 'C++', 'XML', 'PHP']
In the above example print command just has printed all the elements in the order they have placed inside the list. Now if we change the order in the list then the printing order will also be changed accordingly.
# String list example
str_list = ['XML', 'PHP', 'Python', 'Java', 'C', 'C++']
print("\nString list contains -> ", str_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
String list contains -> ['XML', 'PHP', 'Python', 'Java', 'C', 'C++']
In the above example we have changed the position of element XML and the impact is visible in the printed list. So Lists are maintaining the order in which the data are inserted into the list.
NUMBER LIST
Number lists contain all the number elements either Integer or Floating point number.
INTEGER LIST
Integer lists contain all the integer number elements.
# Integer list example
num_list = [4, 6, 2, 10, 15, 20]
print("\nInteger list contains -> ", num_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
Integer list contains -> [4, 6, 2, 10, 15, 20]
Changing the order of elements
# Number list example
num_list = [10, 15, 4, 6, 2, 20]
print("\nInteger list contains -> ", num_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
Integer list contains -> [10, 15, 4, 6, 2, 20]
FLOATING LIST
Floating lists contain all the floating point number elements.
# Floating list example
float_list = [5.8, 2.6, 7.8, 6.3, 9.5]
print("\nFloating list contains -> ", float_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
Floating list contains -> [5.8, 2.6, 7.8, 6.3, 9.5]
BOOLEAN LIST
Boolean lists contains only TRUE and FALSE.
# Boolean list example
bool_list = [True, False]
print("\nBoolean list contains -> ", bool_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
Boolean list contains -> [True, False]
Changing the order of elements.
# Boolean list example
bool_list = [False, True]
print("\nBoolean list contains -> ", bool_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
Boolean list contains -> [False, True]
COMBINED DATA TYPE LIST
List in Python can contain elements of different data types as well.
# Combined data type list example 1
comb_list = ['Python', 10, 12, 5.8, False, 'Java']
print("\nCombined list contains -> ", comb_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
Combined list contains -> ['Python', 10, 12, 5.8, False, 'Java']
In the above example we can see that comb_list variable contains elements of String, Number, Floating number, Boolean data type.
List can also contain another list inside it.
# Combined data type list example 2
comb_list = ['Python', 10, 12, 5.8, False, 'Java', [2, 5, 6], ['XML', 'C++'], [True, False]]
print("\nCombined list contains -> ", comb_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
Combined list contains -> ['Python', 10, 12, 5.8, False, 'Java', [2, 5, 6], ['XML', 'C++'], [True, False]]
In the above example we can see that comb_list contains other multiple lists inside it. The yellow marked list is a Number list, the blue marked list is a String list and the pink marked list is a Boolean list.
DUPLICACY IN LISTS
Lists in Python allow the duplicate values. A list can contain duplicate elements.
# Duplicacy in list example
# String list example
str_list = ['Python', 'Java', 'C', 'Python', 'XML', 'Java']
print("\nString list contains -> ", str_list)
# Integer list example
num_list = [4, 6, 2, 4, 15, 6]
print("\nInteger list contains -> ", num_list)
# Floating list example
float_list = [5.8, 2.6, 5.8, 6.3, 9.5, 2.6]
print("\nFloating list contains -> ", float_list)
# Boolean list example
bool_list = [True, False, True]
print("\nBoolean list contains -> ", bool_list)
# Combined data type list example
comb_list = ['Python', 10, 12, 5.8, 6, 5.8, True, 'Java', True, [2, 5, 6], [2, 5, 6], ['XML', 'C++'], [True, False]]
print("\nCombined list contains -> ", comb_list)
INTRODUCTION TO PYTHON LISTS : Output
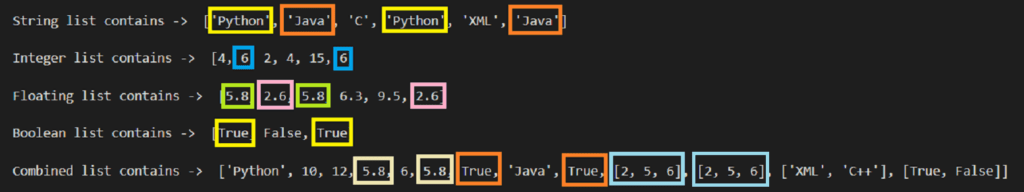
String list contains -> ['Python', 'Java', 'C', 'Python', 'XML', 'Java']
Integer list contains -> [4, 6, 2, 4, 15, 6]
Floating list contains -> [5.8, 2.6, 5.8, 6.3, 9.5, 2.6]
Boolean list contains -> [True, False, True]
Combined list contains -> ['Python', 10, 12, 5.8, 6, 5.8, True, 'Java', True, [2, 5, 6], [2, 5, 6], ['XML', 'C++'], [True, False]]
In the above example we can see that every type of list contains duplicate values.
In String list Python and Java both elements are occurred twice.
In Integer list 6 is occurred twice.
In Floating list 5.8 and 2.6 both are occurred twice
In Boolean list True is occurred twice.
In Combined list the highlighted elements are occurred multiple times including list element containing [2, 5, 6].
RELATED TOPICS:
- ACCESSING PYTHON LISTS
- ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS
- UPDATING PYTHON LISTS
- REMOVING ELEMENT IN THE LISTS
- PYTHON LIST SLICING OPERATION
- USING STEP SIZE IN LIST SLICING OPERATION
- LIST SORTING OPERATIONS
- PYTHON LIST BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS
- REMOVING DUPLICATES USING PYTHON SET OPERATOR
- PYTHON SHALLOW COPY OPERATIONS
- PYTHON LIST DEEP COPY
Pingback: ACCESSING PYTHON LISTS - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: ADDING NEW ELEMENTS IN THE LISTS - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: UPDATING PYTHON LISTS - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: REMOVING ELEMENT IN THE LISTS - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: PYTHON LIST SLICING OPERATION - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: STEP SIZE IN PYTHON LIST SLICING - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: LIST SORTING OPERATIONS - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: REMOVING DUPLICATES USING PYTHON SET - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: PYTHON LIST BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: PYTHON LIST DEEP COPY - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming
Pingback: PYTHON LIST SHALLOW COPY - Sayantan's Blog On Python Programming